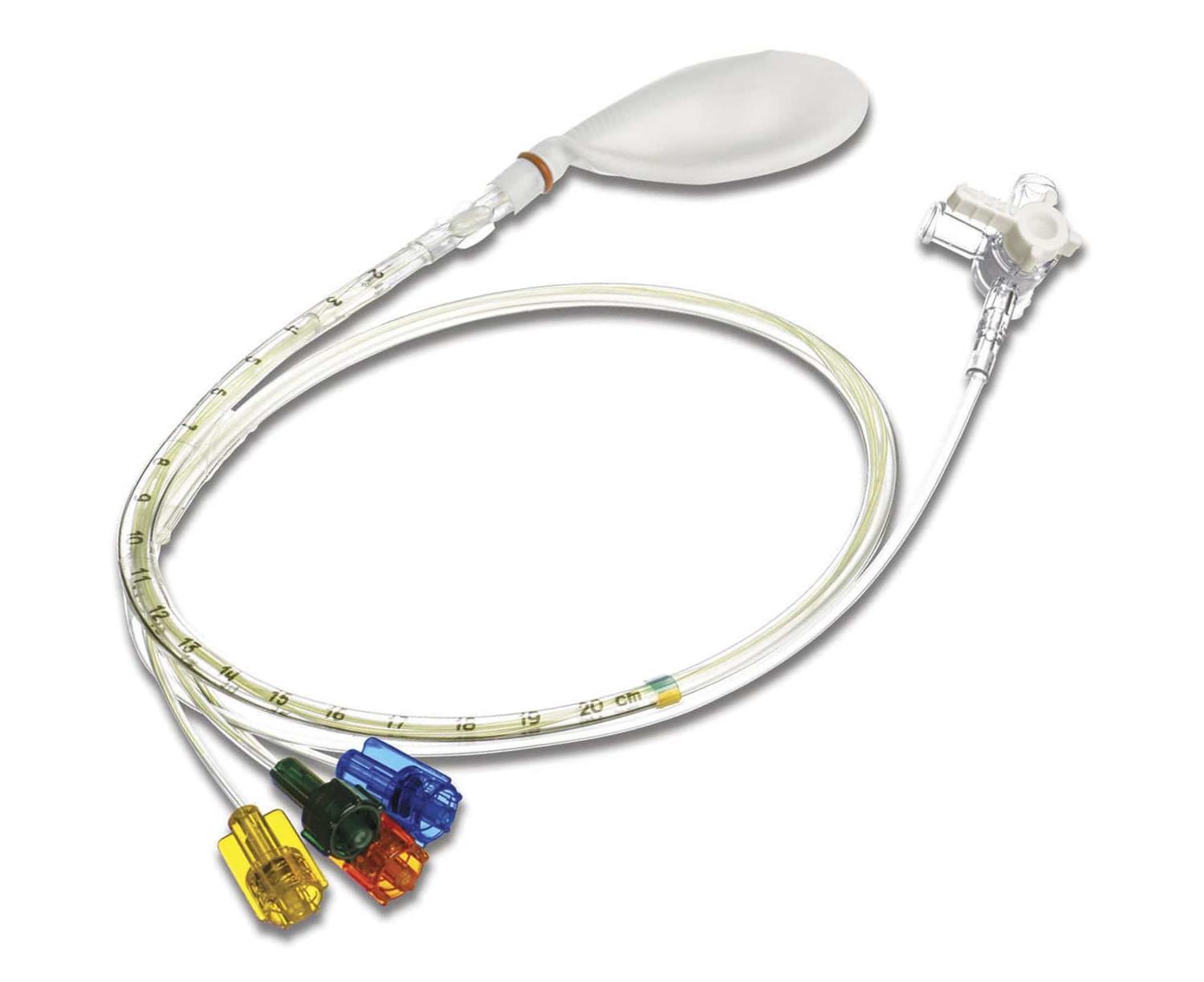
Anorectal manometry is a diagnostic technique that is intended to test how well the rectum and anal sphincter are functioning. In the blog post below, when this test is commonly prescribed, as well as an explanation of the procedure, will be described.
What is Anorectal Manometry?
Anorectal manometry is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that is simple to perform, but it requires complex equipment and well trained nursing staff. This test is used to measure the patient’s contractility in his or her anus and rectum. A catheter with a balloon attached is inserted directly into the patient’s rectum. The balloon is inflated, and pressure readings from the sphincter and rectum are recorded. One purpose of anorectal manometry is to test the ability of the muscles and tissues surrounding the balloon is to relax in response to pressure. For instance, if rectal muscles and sphincter do not relax when the balloon is inflated, paralysis of the colon could be to blame.