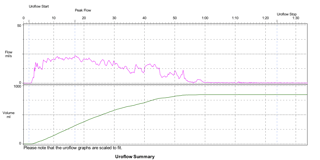
 How can we gauge the current level of diagnostic utility of uroflowmetry? Are there areas needing research to improve it? This study was performed to verify the diagnostic value of uroflowmetry, its flaws, to discuss gaps in knowledge, and to provide areas where further research is necessary.
How can we gauge the current level of diagnostic utility of uroflowmetry? Are there areas needing research to improve it? This study was performed to verify the diagnostic value of uroflowmetry, its flaws, to discuss gaps in knowledge, and to provide areas where further research is necessary.
How Can We Maximize The Diagnostic Utility Of Uroflow?
Topics: Uroflow, Uroflowmetry
Anorectal manometry is a widely-available, economical and precise test for establishing the functional competency of the rectum and the anal canal. It plays an essential role in the diagnosis of functional defecatory disorders such as constipation, fecal incontinence and Hirschsprung disease in children.
This test involves the assessment of two major functions of the anorectal system. The resistive system – continence; and the capacitive system – defecation. Continence and defecation are the two most important roles played by the anorectal system. Quantitative assessment of the anal sphincter tone by anorectal manometry helps find the etiology of anorectal disorders. In the following article, we are going to discuss briefly how to interpret conventional anorectal manometry.
Topics: Anorectal Manometry
 Most of the urodynamic literature is currently focused on the indications for urodynamic studies for treatment of voiding dysfunction and urinary incontinence. In reality, much less is known about the frequency with which urodynamic procedures are being performed and trends in the practice among urologists. In the following article, we will talk about trends in the practice of urodynamic procedures among urologists in the last decade and we will try to find what factors impacting growth. We compared relevant studies and put together the information to assess the utilization of urodynamic procedures.
Most of the urodynamic literature is currently focused on the indications for urodynamic studies for treatment of voiding dysfunction and urinary incontinence. In reality, much less is known about the frequency with which urodynamic procedures are being performed and trends in the practice among urologists. In the following article, we will talk about trends in the practice of urodynamic procedures among urologists in the last decade and we will try to find what factors impacting growth. We compared relevant studies and put together the information to assess the utilization of urodynamic procedures.
Topics: urodynamics staffing, urology, urodynamics service provider
Ambulatory vs. Traditional Urodynamics in Spinal Cord Injuries
 Bladder management is a hugely important factor that needs to be taken into consideration when it comes to managing patients with spinal cord injury (SCI). In the following blog post, we will discuss differences between ambulatory urodynamics and conventional urodynamics on patients with SCI.
Bladder management is a hugely important factor that needs to be taken into consideration when it comes to managing patients with spinal cord injury (SCI). In the following blog post, we will discuss differences between ambulatory urodynamics and conventional urodynamics on patients with SCI.
According to this article1, conventional urodynamic testing has multiple drawbacks mainly due to the unfamiliar circumstances for the individual, immovability of the instrument, expenses, restrictive position during the test as well as manual filling of the bladder (rather than natural filling). Therefore, fully ambulatory urodynamic monitoring systems have been developed, which enable the pressure in the abdomen to be measured in a perfectly non-invasive manner. The question is: how reliable are they and can we use the findings effectively?
Topics: urodynamics, ambulatory urodynamics
Why Urodynamics & UroCuff Tests Are Appropriate For Health Care Today
In the US, over 17 million people suffer from daily urinary incontinence. When discussing the prevalence of incontinence, women are more predisposed to this condition. To get a better grasp on the seriousness of urinary incontinence, take a look at some facts:
- Between the ages of 30 and 59, one in four women has had an episode of urinary incontinence
- More than 50% of elderly people which are living at home or placed in specialized facilities have urinary incontinence
- The good news is that 80% of those affected by urinary incontinence can be cured, or have their life improved.
Topics: Urodynamics Testing, UroCuff
Bladder cancer is a relatively rare phenomenon in the United States – affecting fewer than 200,000 Americans annually – but can be serious when left untreated. Here, incontinence will be discussed relative to bladder cancer, which is a side effect of both the cancer itself and the treatment.
Topics: incontinence, Bladder Cancer
With recent changes to healthcare and reimbursement, interest in management service organizations (MSOs) has increased. In years past, these services have been met with caution, as they were judged to create more risk than reward. However, recently that balance has shifted. Here, ObGyn MSOs will be discussed.
Topics: ObGyn Practices
The Importance of Variable Cost Structures in Medical Practices
When it comes to medical practice, the cost of doing business can be vastly different than for other small businesses. While building revenue is important, so is effective customer service and high-quality patient care.
As the model for reimbursement changes, efficient cost management is becoming a key component of the survival and stability of the independent medical practice.
Here, the types of costs associated with medical practices will be discussed, as well as why the variable cost structure is important.
Topics: General Urology Information, Medical Practice Operations
UroCuff vs. Urodynamics – How They Fit Together and Are Complimentary
Urodynamics Explained
Urodynamics is a blanket term for a series of tests that assess the functionality of the lower urinary tract. Numerous
problems of the bladder and urethra which commonly affect both men and women can be diagnosed via urodynamics. Typically, these tests are ordered to diagnose issues such as urinary incontinence or prostrate problems, as well as before and after any type of surgery involving the pelvic organs or the urinary tract. Common symptoms that result in a doctor ordering urodynamics include incontinence, frequent urination, inability to urinate, weak urine stream, painful urination, nocturia, recurrent urinary tract infections, and difficulties emptying the bladder entirely. The types of urodynamic tests commonly performed include the following:
Topics: urodynamics, UroCuff
When should Anorectal Manometry (ARM) Typically Be Prescribed
Anorectal manometry is a diagnostic technique that is intended to test how well the rectum and anal sphincter are functioning. In the blog post below, when this test is commonly prescribed, as well as an explanation of the procedure, will be described.
What is Anorectal Manometry?
Anorectal manometry is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that is simple to perform, but it requires complex equipment and well trained nursing staff. This test is used to measure the patient’s contractility in his or her anus and rectum. A catheter with a balloon attached is inserted directly into the patient’s rectum. The balloon is inflated, and pressure readings from the sphincter and rectum are recorded. One purpose of anorectal manometry is to test the ability of the muscles and tissues surrounding the balloon is to relax in response to pressure. For instance, if rectal muscles and sphincter do not relax when the balloon is inflated, paralysis of the colon could be to blame.